Way back in 2014 I wrote a Library Technology Report called 3D Printers for Libraries, one of the first long form works that set out to explain 3D printing to librarians. It is licensed under a CC BY-NC license, and 2 years seems like plenty of time for me to avoid linking to a copy here on the blog, so if you’re interested, here’s a PDF copy of it for you.
Since then, the market for 3D printers has exploded, but there have emerged a few new leaders that weren’t as well established when I wrote the LTR. Since that report was released, my favorite printers and the ones that I recommend for libraries are the Lulzbot Mini and Lulzbot Taz 6…they are spectacular FDM printers, capable and easy to use. Even better, they are certified Open Hardware and use Open Source software top to bottom, which means that they are easily repaired and have a myriad of options for printer management, slicing, and control.
One of those options is something that I’ve not seen recommended for libraries, but that I feel like they and others could get a huge amount of mileage from. Octoprint is an open source control program for 3D printers that runs on a variety of hardware (there are install instructions for Windows, OS X, and Linux) but by far the most interesting and useful method for using it is via the OctoPi project that uses a Raspberry Pi as a host for the Octoprint system and all its requirements. You can download pre-built images for a Raspberry Pi, flash an SD card, boot up the Pi, and have a robust and flexible management system for your 3D printer ready to go.
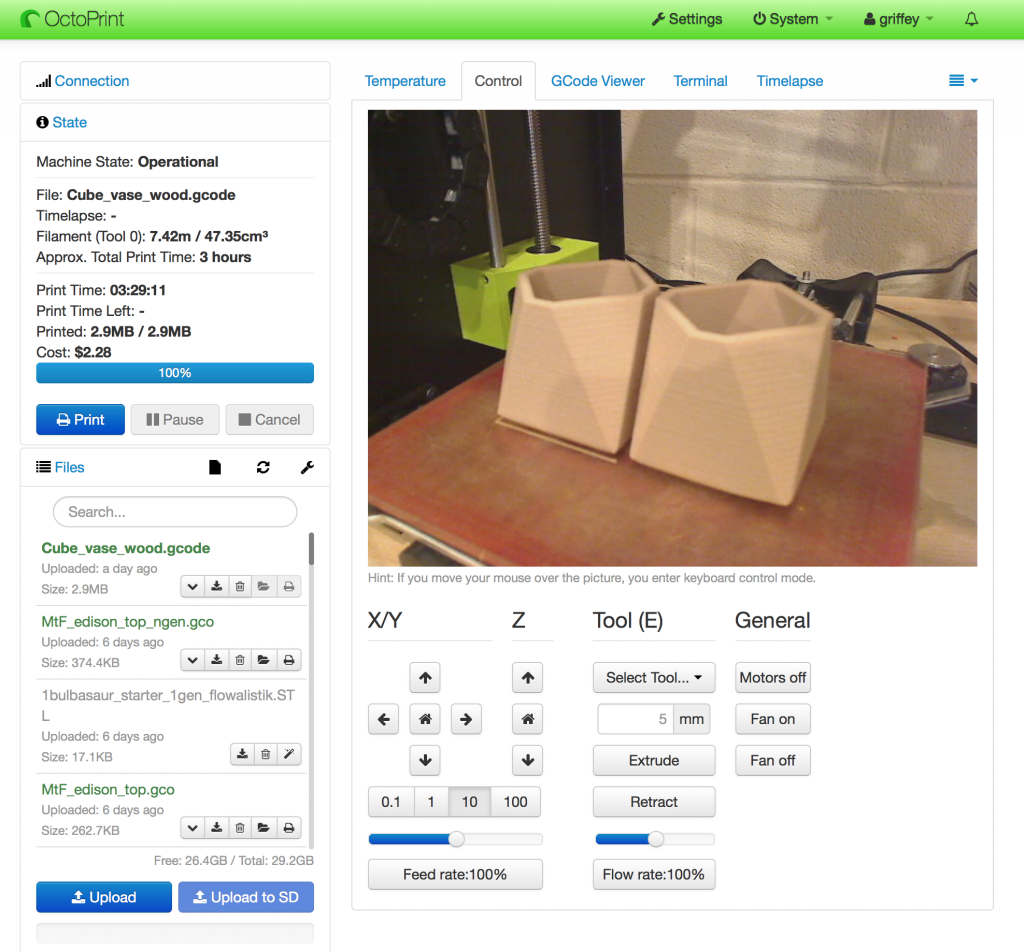 What does Octoprint do? For compatible printers (which includes nearly any that use the industry standard gcode instructions to print), Octoprint can control every aspect of the printer, including:
What does Octoprint do? For compatible printers (which includes nearly any that use the industry standard gcode instructions to print), Octoprint can control every aspect of the printer, including:

- Print queuing
- Slicing
- Physical control (movement of printhead, temperature, etc)
- Gcode previewing, including printhead movement
- Start, stop, and pause prints
- Full plugin architecture that allows for everything from cost estimation and filament usage, printer usage statistics, and integration with a variety of messaging apps (get Slack notifications when a print is completed, for example)
- Native support for video streaming via an attached webcam, including the ability to use the same camera for time lapses of your prints

The best part? All of the above take place in a web browser. No client software needed, no keeping up with installs of Cura or other printer-specific software. Suddenly you can start a print or monitor your printer from anywhere on your network, or from anywhere in the world if you forward the appropriate port externally. I recently uploaded and started a new print on the printer in my basement while in a different hemisphere…
You can preset the available plastic types and quality settings through printing profiles for slicing of uploaded STL files. For my part, since my primary printer is a Lulzbot Mini, I just downloaded the profiles directly from the manufacturer and uploaded them to Octoprint, and can now upload any STL that I find directly to my printer, from anywhere I am in the world.
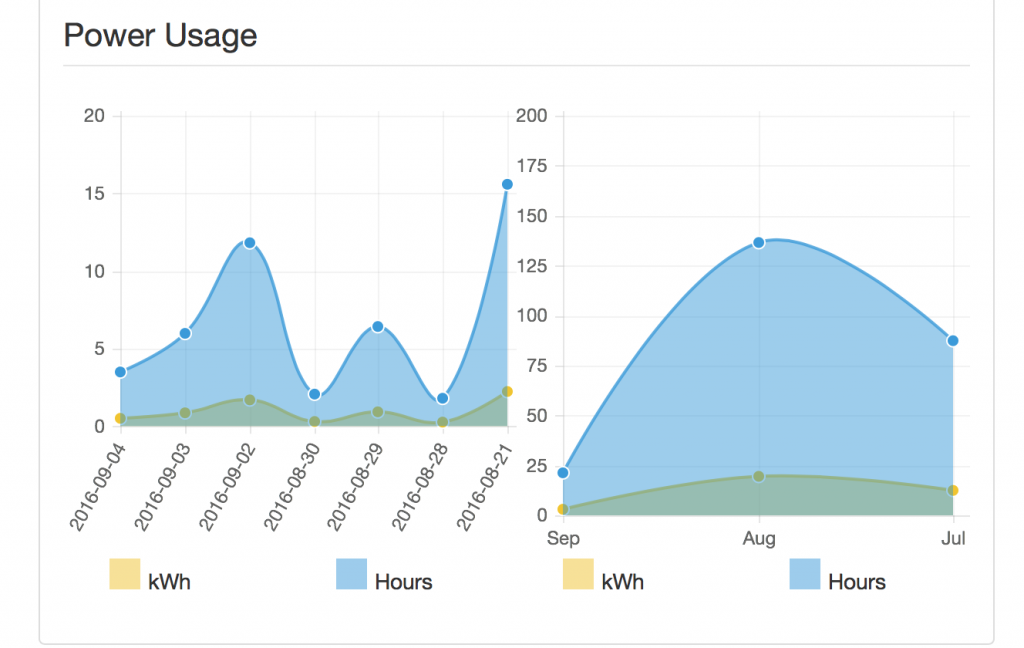
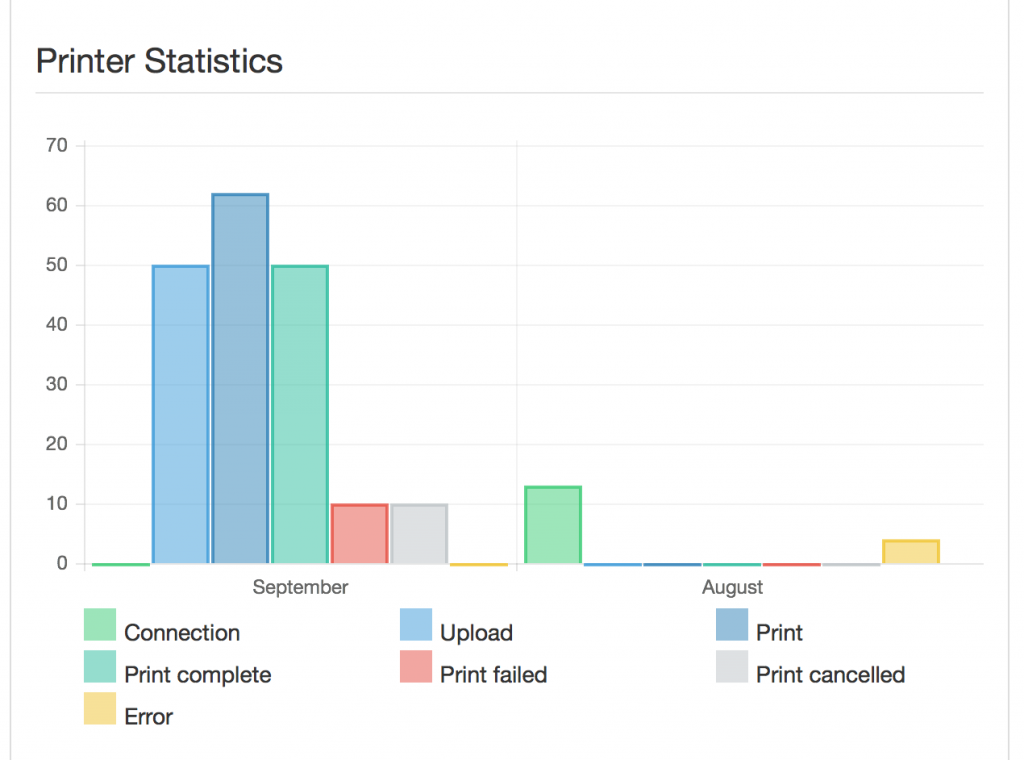
For most libraries, just the ease of statistics and usage tracking would be enough to make Octoprint useful enough to try out.
But add in the ability to control your printer(s) from any computer, to video stream the printing and watch for errors remotely, to be alerted when a print completes…it’s just a much more robust way of managing your 3D printing. And for the cost of a Raspberry Pi and maybe an hour of setup, you can be up and running.
This isn’t to say that Octoprint solves all 3D printing problems. It’s largest shortcoming in my opinion is its lack of plating tools…if you have an STL, you are stuck with just printing that single STL with Octoprint. If you need to plate several STL files together on a single print plate, you would have to do that in Cura or other program (you could even do it in Tinkercad if you wanted to stay in-browser I suppose) and then either save the collection as an STL or go ahead and slice it to gcode and upload the gcode directly to Octoprint. It is technically possible for a single install and Raspberry Pi to control more than one 3D printer, but it isn’t built in to the system and is something I’d only recommend to technical users. RPi’s aren’t expensive, and having one per printer isn’t the end of the world, but hopefully over time the OctoPi setup will evolve to handle multiple printers natively.
I’ve been using the latest version of Octoprint for months now, and it’s simplified so much of my work with my 3D printer. If you are responsible for running the makerspace or 3d printer service in your library, check out Octoprint. I’m guessing it will make your life easier.
I’m considering putting together a workshop on how to install and use Octoprint with your 3D printer…would anyone be interested in such a training? If so, leave me a comment and let me know, I’ll see if I can find a venue and do it sometime this winter.

